

The second result shows that the path of light traveling through a magnetic field in a vacuum bends differently depending on how that light is polarized. Now scientists have converted light energy directly into matter in a single step. Nuclear reactions in the sun and at nuclear power plants regularly convert matter into energy. This conversion of energetic light into matter is a direct consequence of Einstein’s famous E=mc 2 equation, which states that energy and matter (or mass) are interchangeable. The primary finding is that pairs of electrons and positrons-particles of matter and antimatter-can be created directly by colliding very energetic photons, which are quantum “packets” of light. The results were derived from a detailed analysis of more than 6,000 pairs of electrons and positrons produced in glancing particle collisions at RHIC and are published in Physical Review Letters. Department of Energy Office of Science user facility for nuclear physics research at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory-have produced definitive evidence for two physics phenomena predicted more than 80 years ago. UPTON, NY-Scientists studying particle collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC)-a U.S. As the ions pass one another without colliding, two photons (γ) from the electromagnetic cloud surrounding the ions can interact with each other to create a matter-antimatter pair: an electron (e -) and positron (e +).
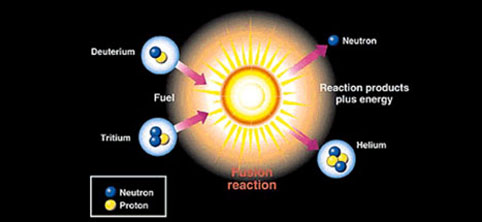
It also describes how these concepts apply to the work that the Department of Energy’s Office of Science conducts as it helps the United States excel in research across the scientific spectrum.Making matter from light: Two gold (Au) ions (red) move in opposite direction at 99.995% of the speed of light (v, for velocity, = approximately c, the speed of light). DOE Explains offers straightforward explanations of key words and concepts in fundamental science. Learn about joint DOE-private sector efforts to advance fusion power in these presentations from a June 2022 workshop.Science Up-Close: Developing a Cookbook for Efficient Fusion Energy.DOE Office of Science Fusion Energy Sciences program This is like throwing a perfect strike in baseball from a pitcher’s mound 350 miles away from the plate. Fusion reaction experiments at the DOE’s National Ignition Facility at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory require 192 laser beams to align on a DT target smaller than a pea.“Burning plasmas” in ITER will be heated by the fusion reactions occurring in the plasma itself. The ITER international fusion energy experiment will be scientists’ first attempt at creating a self-sustained fusion reaction for long durations.FES also partners with the DOE’s National Nuclear Security Administration to pursue fundamental research on fusion reactions in support of DOE’s nuclear stockpile stewardship mission. They work with the Advanced Scientific Computing Research program to use scientific computing to advance fusion science as well as the Nuclear Physics program on nuclear reaction databases, generation of nuclear isotopes, and research in nucleosynthesis. To do so, FES partners with other Office of Science programs. The Department of Energy Office of Science, Fusion Energy Sciences (FES) program seeks to develop a practical fusion energy source. Researchers focus on DT reactions both because they produce large amounts of energy and they occur at lower temperatures than other elements. In a potential future fusion power plant such as a tokamak or stellarator, neutrons from DT reactions would generate power for our use. In the process, it also releases much more energy than most fusion reactions. DT fusion produces a neutron and a helium nucleus. However, researchers working on fusion energy applications are especially interested in the deuterium-tritium (DT) fusion reaction. If scientists develop a way to harness energy from fusion in machines on Earth, it could be an important method of energy production.įusion can involve many different elements in the periodic table. Einstein’s equation (E=mc 2), which says in part that mass and energy can be converted into each other, explains why this process occurs. The process releases energy because the total mass of the resulting single nucleus is less than the mass of the two original nuclei. The leftover mass becomes energy. In a fusion reaction, two light nuclei merge to form a single heavier nucleus. Nuclear Fusion reactions power the Sun and other stars.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
